Ecological Values
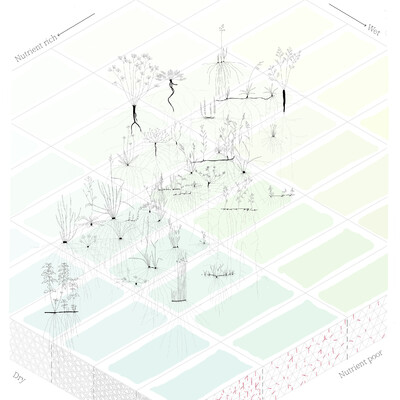
Ecological values ("Ökologische Zeigerwerte") is a classification method for Central European plants according to their ecological behavior and botanical characteristics, first described by Heinz Ellenberg in 1974. The numbers give an indication of the preferred soil and climate conditions of a plant, such as soil moisture, pH and nutrients as well as light and temperature.
We are using this concept to better understand the garden's plants and its habitats. We have translated the ecological values into a color map, focusing on the values for soil moisture (dry - wet) and nutrients (nutrient rich - nutrient poor). These are the most decisive factors for the garden on the Hönggerberg, while the climate values are rather homogeneous across the entire plot. The map also contains info whether the plant can withstand large fluctuations in the water balance (dashed line). We have then added some of the plants that we have identified in our garden to the map to analyze the various conditions the represent. As expected, we see that they cover various soil conditions, but most of the plants in our garden grow in zone 3:4 - medium moisture and rather nutrient-rich. The concept of ecological indicator values should be understood as a qualitative gradient rather than as absolute quantitative values. That's why it is interesting to compare the ecological values with observations in practice.